
Welcome to Metabomizer
Overview
Drug discovery and development is a labor-intensive process that typically spans about a decade, including 6-8 years of clinical trials and costs that can exceed $2.6 billion. This extensive timeline and high expense present significant challenges in optimizing lead compounds rationally.
The development of small molecule oral drugs is of great significance in the pharmaceutical industry. Optimizing lead compounds into forms that are orally bioavailable represents a critical phase in this process. This involves a comprehensive evaluation of several physiological processes, including oral absorption, first-pass metabolism, and systemic distribution.
When drug candidates are administered orally, they undergo extensive metabolism in the human body, with the liver and gastrointestinal tract serving as the primary metabolic organs of concern. Oral drug absorption is influenced not only by physicochemical properties such as solubility and permeability but also significantly affected by first-pass metabolism, which can substantially reduce bioavailability.
The evaluation of chemotoxicity encompasses a comprehensive assessment of both parent compounds and their metabolites, as metabolic products may exhibit different toxicological profiles compared to the original drug candidates. This dual assessment is crucial for ensuring drug safety throughout the metabolic pathway.
Each of these factors plays a crucial role in determining the drug's efficacy and safety profile. Accurate prediction and assessment of these processes are essential for pharmacological optimization, ensuring that the drug achieves the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing potential adverse effects.
Traditionally, medicinal chemists have depended on personal experience to guide optimization, a method that may be low efficiency. To overcome this challenge, researchers have turned to artificial intelligence methods, leveraging extensive public databases and computational approaches.
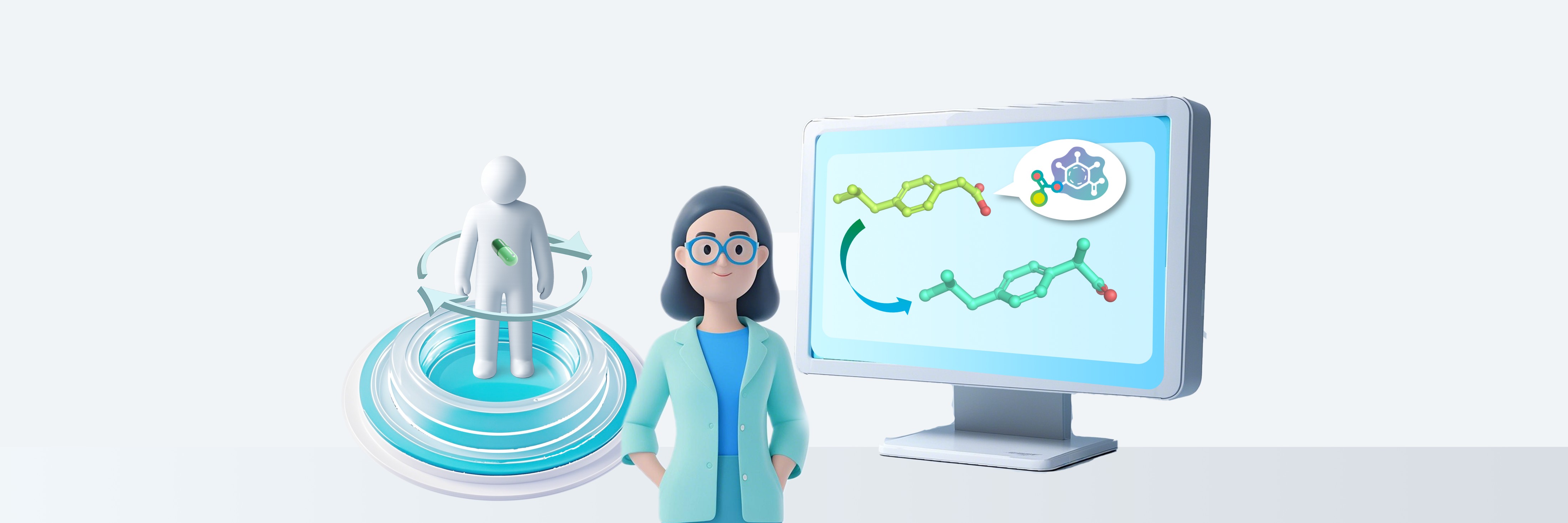
Therefore, our platform conducts integrated assessments of compound toxicity and oral bioavailability while predicting potential metabolites. Additionally, we provide an intelligent optimization scheme for candidate compounds, enabling rational drug design through comprehensive in silico evaluation backed by the most extensive metabolic database available.
Metabolism prediction and modification
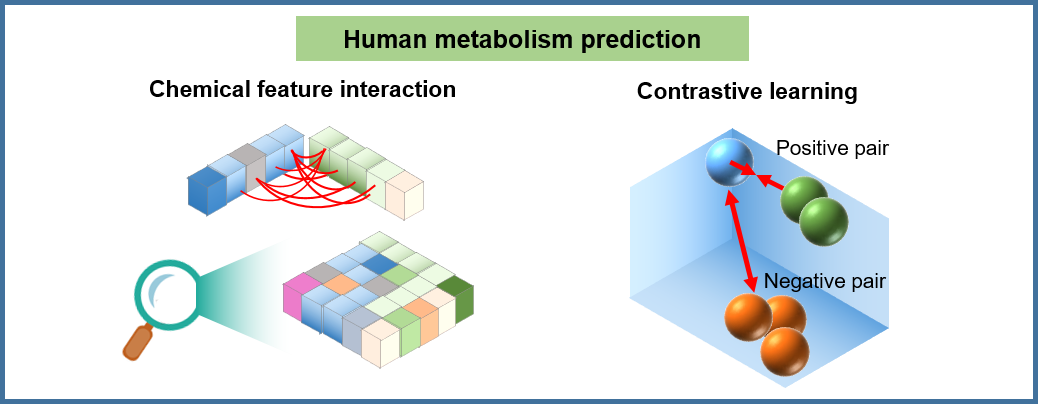
🎯 Advanced metabolism prediction model ConMeter: Our deep learning model leverages contrastive learning to predict metabolic products with unprecedented accuracy.
Template Library Analysis
We utilized a comprehensive human-specific drug metabolism database containing 11,665 metabolic reactions categorized into 17 reaction types to create 2,497 high-quality, non-redundant reaction rules. These rules integrate existing expert knowledge from sources like SyGMA and GloryX, enhancing the coverage of metabolic transformations. Unlike traditional expert rules, which can be complex and difficult for medicinal chemists to interpret, our templates match 4,214 reactions from both open-source databases and our curated collection. Each template is annotated with its reaction type and source, greatly simplifying the understanding of metabolic transformations.
* Hover over the chart segments to view detailed information about each reaction type.
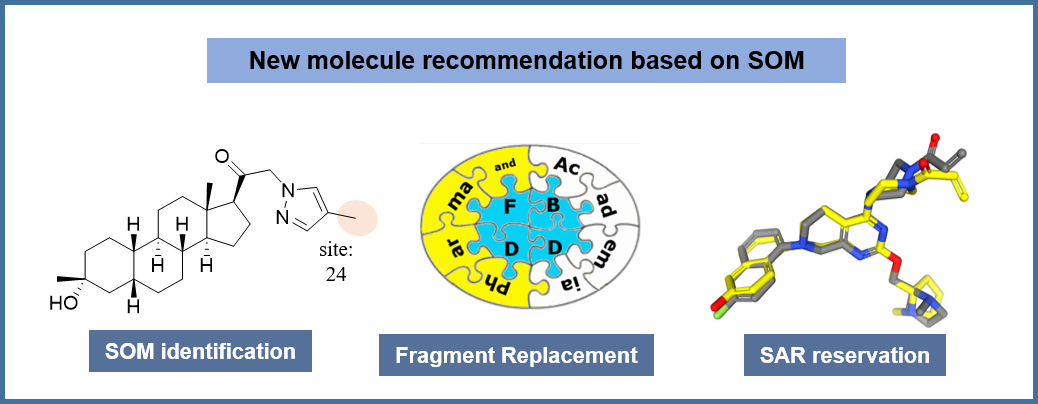
🔬 Intelligent molecular optimization framework: Our molecular optimization framework employs advanced BRICS fragmentation enhanced with MacFrag algorithm to identify metabolic sites with precision. Built on a massive fragment library of 10,378,665 unique fragments derived from 133,373 validated molecules across PubChem, BindingDB, and DrugBank databases. The process involves intelligent fragment categorization, efficient Tanimoto coefficient-based similarity searches, and SHAFTS-powered 3D conformational screening. Key advantage: Largest fragment library in the field enabling comprehensive chemical space exploration with multi-dimensional evaluation combining 2D/3D similarity, drug-likeness, and synthetic feasibility.
Property prediction models
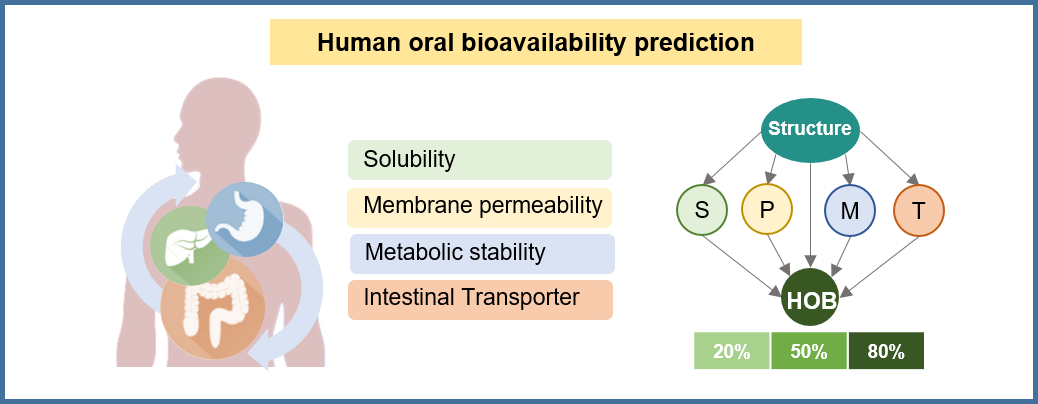
📊 Hybrid deep learning for bioavailability prediction: A hybrid deep learning model was developed for oral bioavailability prediction at multiple thresholds (20%, 50%, 80%). The architecture integrates deep feature extraction capabilities with established physicochemical parameters through transfer learning. Trained on a curated dataset of 1,851 molecules with experimental F values from our internal high-quality database, ensuring reliable predictions based on real-world bioavailability data. Key advantage: Multi-threshold prediction with enhanced accuracy through hybrid architecture combining deep learning and traditional ADMET parameters.
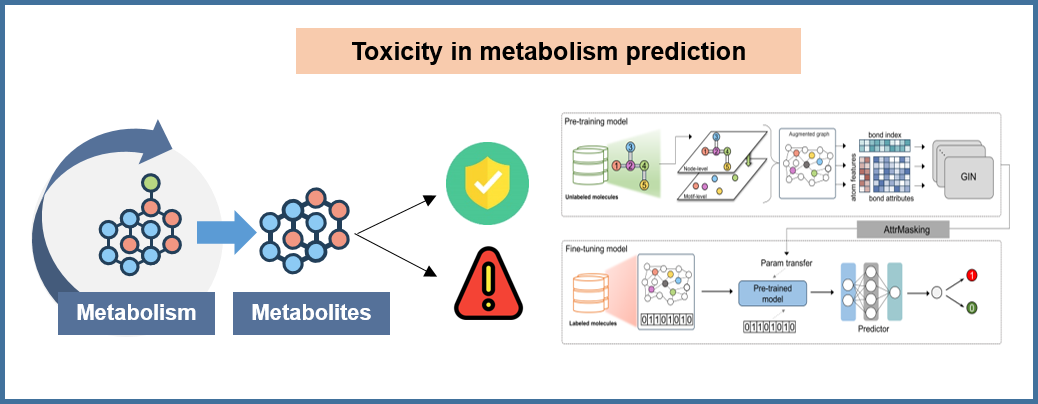
⚡ SGMTox: Self-supervised toxicity prediction: Our toxicity prediction framework, SGMTox, utilizes hierarchical self-supervised learning on molecular graphs and motifs. Pre-trained on the DeeHM metabolite dataset and fine-tuned on our specialized MetaTox dataset containing 2,329 compounds with validated toxicity labels from literature, HSDB, and T3DB databases. The dataset includes both endogenous (1,440 compounds) and exogenous (889 compounds) metabolites, ensuring comprehensive coverage of metabolic toxicity patterns. Key advantage: Superior generalization capability through self-supervised pre-training on the largest metabolites dataset, ensuring reliable assessment for both parent compounds and their metabolites.